You're just a click away!
- Loan within 30 min
- Minimal Documentation
- A Quick, Secure & Transparent Process
Background
We, R.K. Bansal Finance Private Limited , an RBI registered NBFC committed to providing personal loans to employed professionals. We easily meet your unique financial needs by incorporating innovation into the credit availing process, giving you instant access to funds directly. We offer loans at affordable interest rates due to a minimal risk profile. At Ram Fincorp, we take pride in offering the lowest interest rates to our borrowers, ensuring they are not unnecessarily burdened by high interest rates.
Purpose of Manual
The purpose of this document is to provide a detailed description of the target customer profile for this product, sourcing strategy, customer selection criteria, product and program offering, detail credit and risk norms, risk mitigation and provide a high-level business process flow.
Recent Trends
While the Indian economy has traditionally been a cash-based economy, this trend is fast changing. Non- cash-based payments have been registering an upward trend in recent times. India’s digital payment system is expected to be worth around $500 billion by 2020. The digital payments sector is expected to contribute to 15% of India’s gross domestic product (GDP) in four years’ time. Multiple factors and official & behavioral trends are fueling this shift towards a cashless economy.
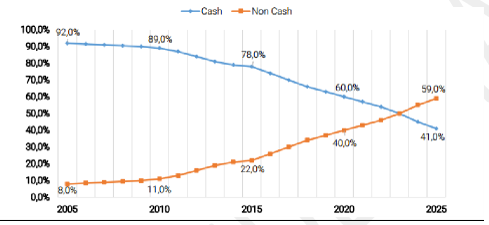
Enhanced internet connectivity, high rate of penetration of smartphones and flagship government initiatives such as ‘Digital India’ have been acting as key catalysts for this change. In fact, it is expected that non-cash payments which constitute 22% of all user payments right now will overtake cash transactions by 2023.
(* Source: Digital Payments 2020 – A report by BCG & Google)
Digital Economy – key Enablers
There are 5 key enablers which have hastened the transformation to a digital economy.
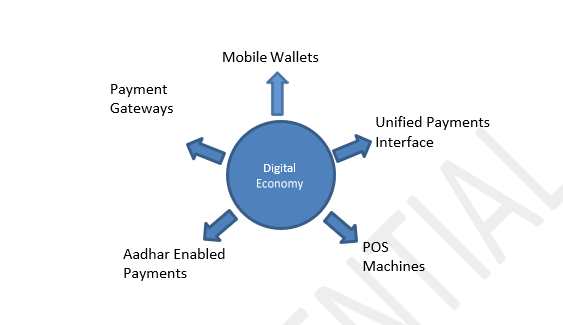 Payment Gateways
Payment Gateways
Mobile Wallets
Unified Payments
Interface
Aadhar Enabled Payments
POS
Machines
a) Payment Gateways:
A payment gateway is a merchant service provided by an e-commerce application service provider that authorizes credit card or direct payment processing for e-businesses, online retailers, bricks and clicks, or traditional brick and mortar.
Online ticketing companies were the first to introduce a significant population to digital payments, by pushing Indian users to get familiar with transacting online for routine services.
This includes transportation such as booking tickets for railways (IRCTC), airlines (MakeMyTrip, Yatra), and buses (RedBus), movie and event ticketing (BookMyShow), and in recent times utility bills payment portals (Bill Desk, Paytm, Citizen Portal, PayU, Oxigen Wallet).
The arrival of online shopping changed the allure of digital payment transactions in India.
Shopping websites like Flipkart, Snapdeal, Amazon, Myntra, Jabong and others, offer highly discounted range, and digital payment such as cash back deals.
b) Mobile Wallets
With the affordable access to smartphones, mobile wallet companies began entering each sector.
The main point was the useful storage of money in digital wallets that made online transactions easier and faster.
Leading mobile wallet companies include Paytm, Mobikwik, Oxigen wallet, Citrus, Freecharge, and PayUMoney.
Today these companies have turned their focus into motivating their users to transact using their service at retail outlets, local grocery stores, restaurants, petrol filling stations, and app-based transport aggregators.
c) Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
Launched by National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), UPI is a rather big accomplishment for RBI, especially because it simplifies and unifies the online money transfer process.
UPI is a payments system that allows money transfer between any two bank accounts by using a smartphone app, without the hassle of typing credit/debit card details, IFSC code, or net banking/wallet passwords. Instead, consumers need to register their mobile number with the bank.
UPI also supports pull and push type of payment requests.
d) Aadhar enabled payments
‘Aadhar Payment Bridge (APB)’ helps make payments directly to the Aadhar enabled bank accounts of people.
‘Aadhar Payment System (APS)’ can provide their Aadhar number and fingerprints at a micro ATM to benefit financial services.
While the authentication is done by UIDAI, the financial transactions are handled by NPCI.
e) POS Machines (Credit/ Debit Card Swipe)
Demonetization has created the need for a shift to digital transactions, its surprise element depriving cash of the security and confidence it once enjoyed as a legal tender. A point of sale terminal (POS machine) is an electronic device used to process card payments at retail locations. A POS terminal generally does the following:
1. Reads the information of a customer’s credit or debit card
2. Checks whether the funds in a customer’s bank account are enough
3. Transfers the funds from the customer’s account to the seller’s account (or at least, accounts for
the transfer with the credit card network)
4. Records the transaction and prints a receipt
As of May’18, there were 13.76 crore credit card transactions and 35.21 crore debit card transactions at POS machines in India, with the total number of POS machines being 32.47 Lakhs in May 2018, almost double from 15.11 lakhs machines that were functioning as of Oct’2016, a month before demonetization.